- Home
- About Us
- Key Business
- Innovation
- Investors
- Investments
- Press Releases
- Qualification & Honor
- Party-mass Collaboration
- Incorruptible
- Contact Us
0571-89939661
Stock code:002266

The R & D team of Zhefu Nuclear Power consists of sub-teams specialized in product design, performance demonstration, manufacturing process research, test verification, etc. Each sub-team is further divided into several groups based on the type of product developed by them. With a common career dream, the Research and Development team currently has more than 70 full-time employees and features a congenial working environment and smooth collaboration. It has successfully developed the main pump of China's first commercial sodium-cooled fast reactor, the lead-bismuth electromagnetic pump, and components of pool-type reactors for low-temperature nuclear heat, and continued to expand the business into new product segments.
We provide ten sets of main nuclear reactor pumps and two sets of reactor components per year. Covering an area of 38,000m², the manufacturing plant is equipped with more than 40 sets of core equipment, including industry-leading laser welding machines, narrow gap welding machines, a custom-made Φ1.5×12.5 tankless and pre-vacuum well-type resistance furnace, the PAMA3800 five-axis CNC milling and boring machine, large horizontal lathes, and large dynamic balancing machines.
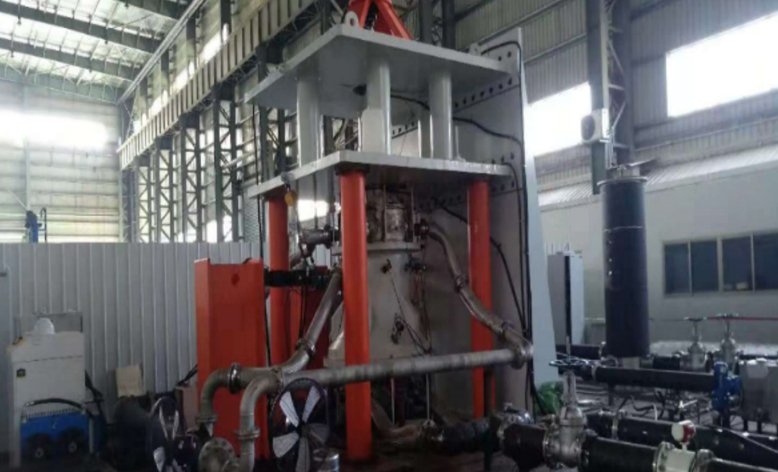
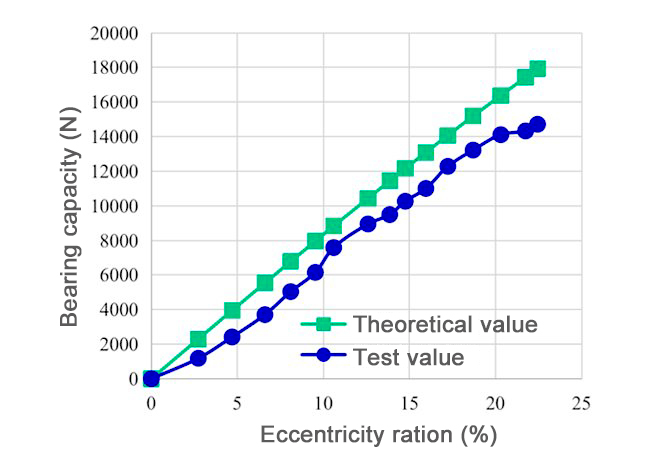
Zhefu Nuclear Power independently developed the lubrication property analysis program for gap throttling and capillary throttling hydrodynamic and hydrostatic journal bearings, and built a performance test bench for vertical slide bearings, which can test the capacity, stiffness, and damping factor of hydrodynamic and hydrostatic journal bearings. Based on the above, sodium-lubricated and lead-bismuth-lubricated hydrodynamic and hydrostatic journal bearings have been developed and put into practical use, and their performance has become industry-leading.

Zhefu Nuclear Power has developed the welding process for cobalt- and nickel-based high-temperature resistant cemented carbide powder, and complete welding for curved surfaces such as planes, and inner and outer cylindrical surfaces. The maximum welding area is more than 2㎡, the welding thickness is up to 7mm, the surface hardness is more than 45HRC, the hardness uniformity is less than 3HRC, and no visible cracks on the surface are detected through PT.
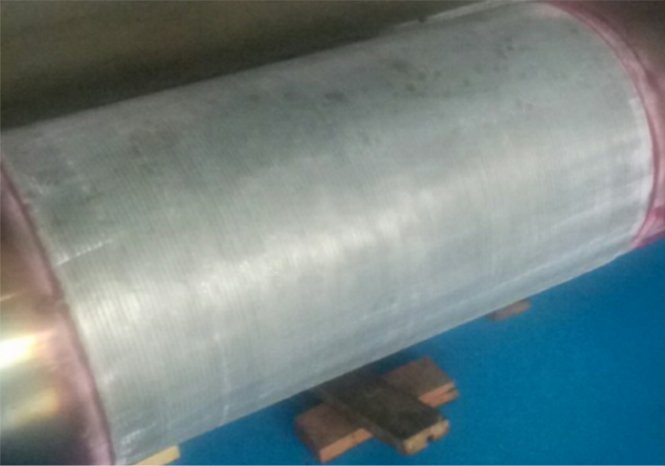
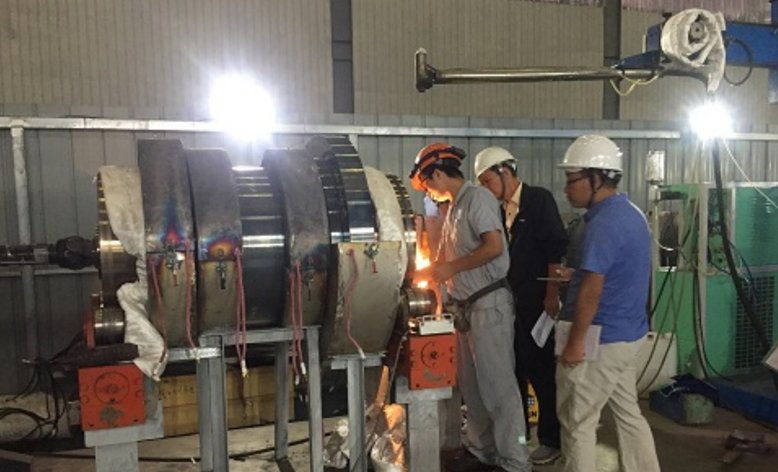


Zhefu Nuclear Power has enabled deformation control in welding and aligning of ultra-long, large-diameter, multi-section shafts. Based on this capability, it has successfully completed manufacturing two-section hollow shafts with a diameter of 800mm and a length of 12m, and controlled its dynamic balance accuracy to G1.6.
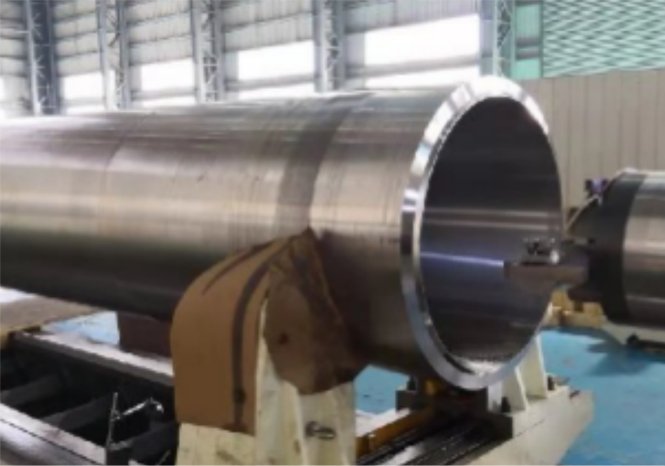
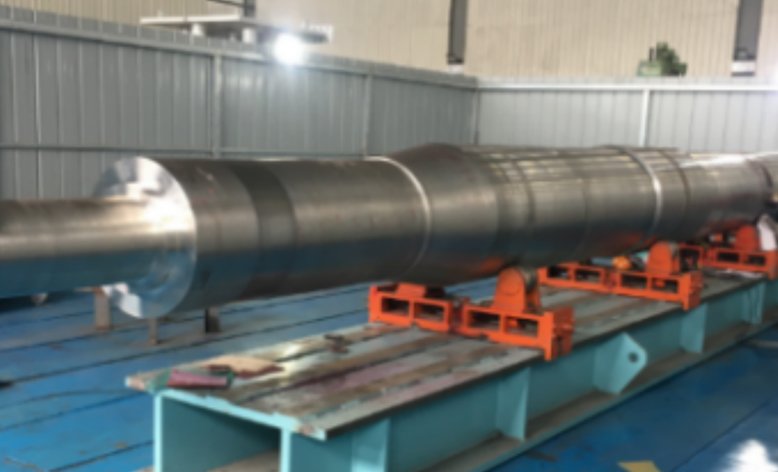


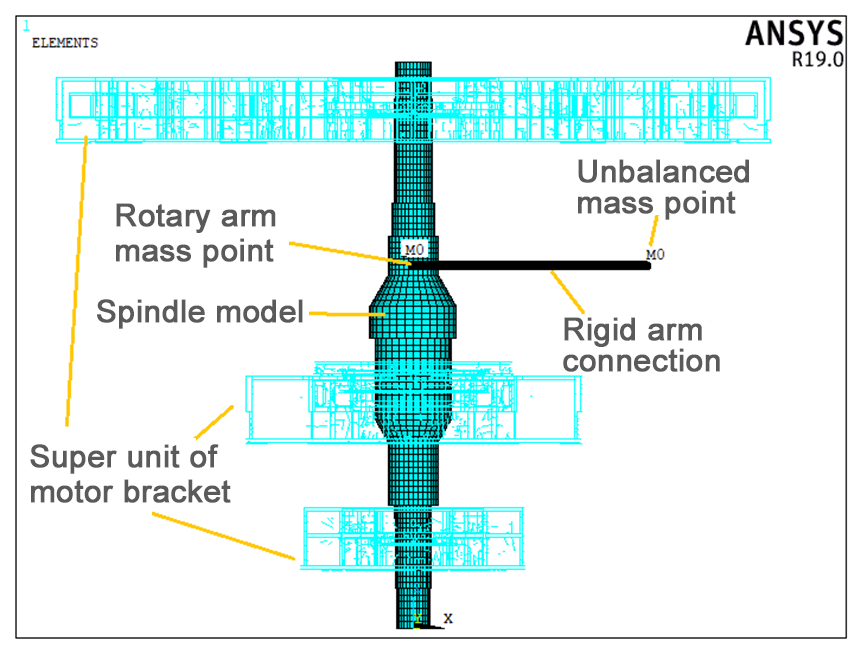
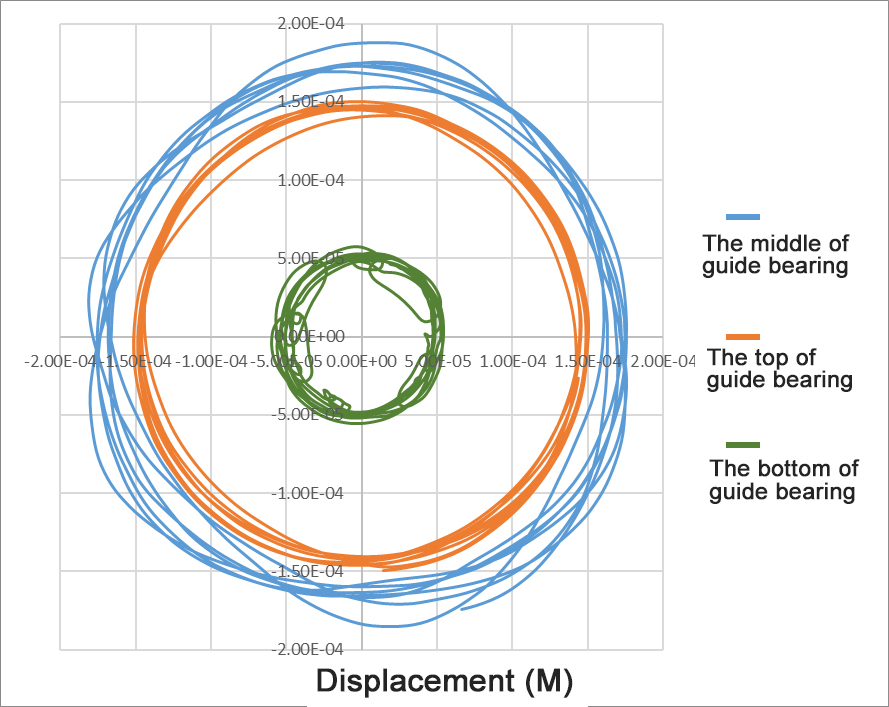
Zhefu Nuclear Power has the ability to equate the radial bearing into a two-vector spring unit and damping unit coupling, establish a characteristic curve between the position of the shaft center and the characteristics of the bearing, and dynamically simulate the movement trajectory of the shaft center. Zhefu Nuclear Power has the ability to equate the radial bearing into a two-vector spring unit and damping unit coupling, establish a characteristic curve between the position of the shaft center and the characteristics of the bearing, and dynamically simulate the movement trajectory of the shaft center.